Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) and Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) compared

Permission Management: How ABAC and RBAC work
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC uses an authorization model that takes into account attributes of the user, the resource, the requested action, and the operational context. Instead of following fixed rules, access decisions are calculated dynamically by interpreting policies that combine real-time variable conditions. This approach makes the system extremely flexible and adaptable, ideal for environments where scenarios and requirements change quickly or are complex.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC is based on predefined roles built according to organizational functions. Each role contains a set of permissions and users automatically receive the rights corresponding to their position. The hierarchical and relatively static structure makes access management simple, intuitive, and easily scalable, particularly suitable for organizations with well-defined and stable tasks.
Fundamental differences between ABAC and RBAC
The key difference between these two models lies in how access decisions are made. The RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) model groups users into predefined roles and assigns standardized permissions. While this approach provides less detailed control, it is easy to manage when user privileges remain relatively stable over time.
In contrast, ABAC (Attribute-Based Access Control) evaluates authorizations in a more targeted and contextual manner, considering attributes such as time, location, or specific characteristics of resources. This allows flexible and precise control, ideal for systems that require frequent adjustments or context-sensitive management.
Ready-Made Templates
Are you looking for an IAM System?Visit Yookey’s website to discover the available solutions
Policy Maintenance: ABAC Flexibility vs RBAC Stability
Access Policy Management highlights a clear difference between the structured approach of RBAC and the dynamic approach of ABAC. The RBAC model offers stability and simplicity in access management, as permissions are static and tied to predefined roles. This makes it relatively easy to implement and reduces administrative overhead, especially when assigning or revoking permissions due to employee role changes.
ABAC provides more granular and flexible control by basing decisions on real-time dynamic attributes. This ability to quickly adapt to contextual conditions makes it particularly suitable for dynamic environments. It should be noted, however, that ABAC involves greater implementation complexity, requiring the continuous definition and management of numerous attributes and policies, which can result in significant administrative workload. To balance stability and flexibility, many organizations adopt a hybrid approach, using RBAC for basic access and ABAC for more sensitive systems that require finer, context-aware control.
Access Control Model Scalability: technical comparison between ABAC and RBAC
Regarding scalability, RBAC is generally considered effective in large organizations with clearly defined roles, as management occurs at the role level rather than for individual permissions. This simplifies administration when the role structure remains relatively stable.
ABAC is regarded as highly scalable and particularly suited to dynamic and diverse environments, such as cloud services. Since access is based on policies defined through attributes, ABAC can easily accommodate an increase in users and resources without requiring significant changes to the existing policy configuration.
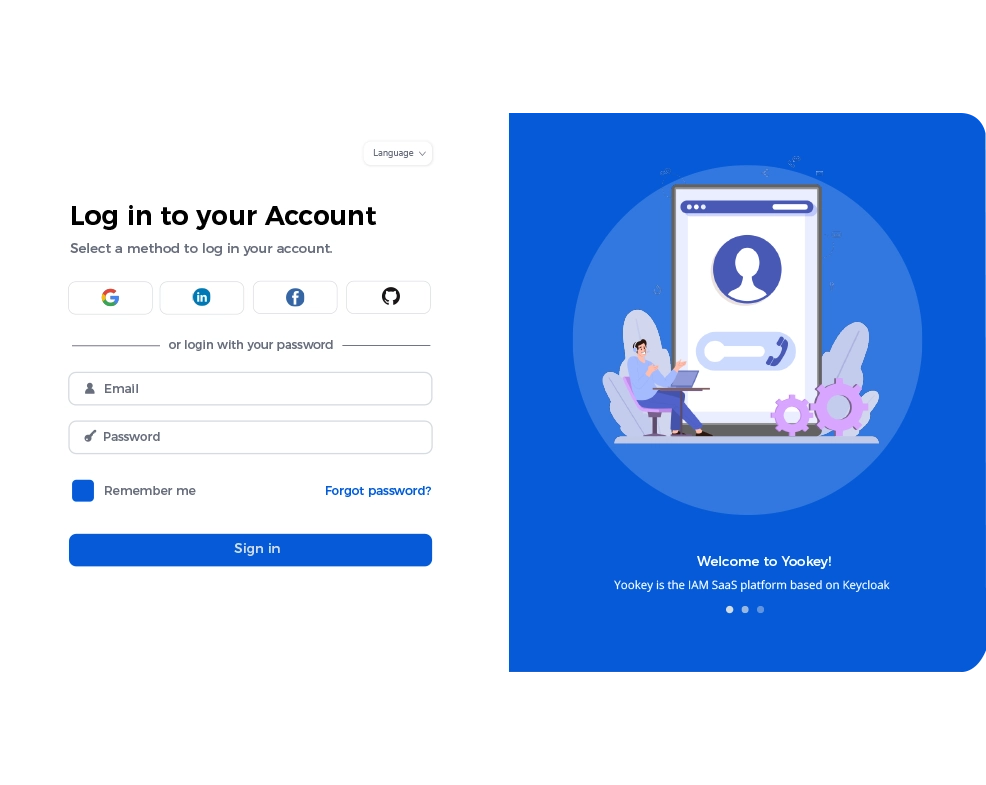
Secure Access Management with Yookey
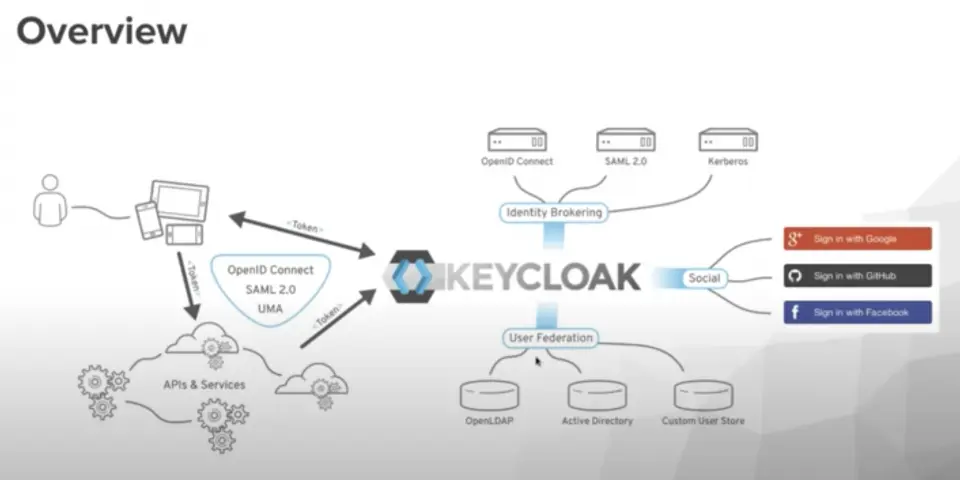
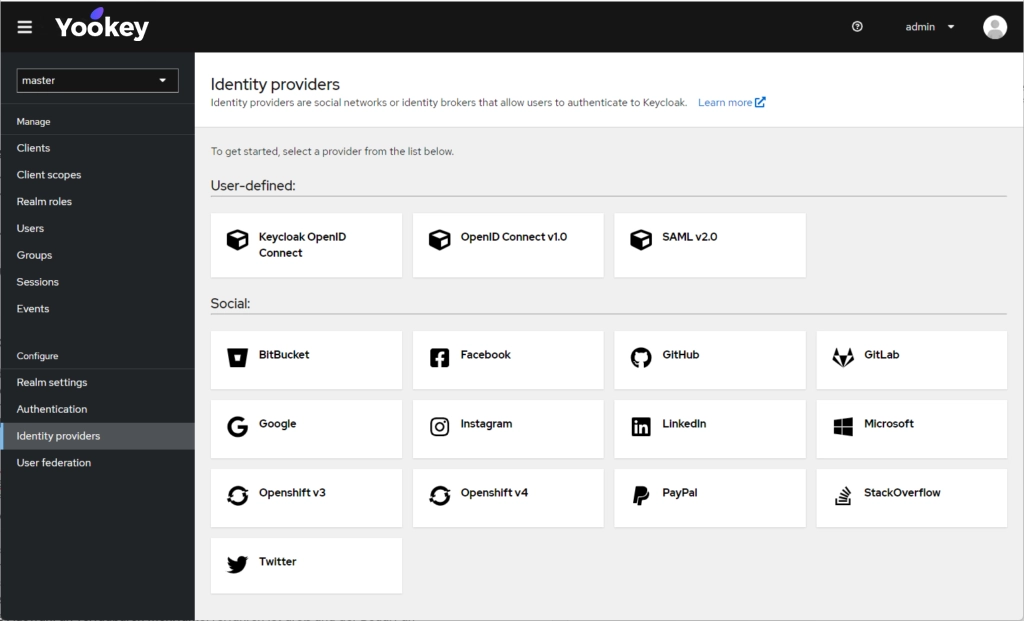
Yookey is an Identity & Access Management (IAM) platform based on Keycloak in SaaS mode, designed to centralize user authentication and authorization. The solution includes advanced features such as Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
The platform also supports integration with corporate directories such as LDAP and Active Directory, as well as national identity systems like SPID and CIE, ensuring security, regular updates, scalability, and GDPR compliance. For permission management, Yookey implements RBAC, assigning privileges to individual roles. This approach ensures centralized management, granular access control and full compliance with corporate policies.
Talk directly with our team for more information.